
|
|

|
The platypus is generally a solitary animal with its own
specific home range in which it feeds and lives. The
platypus is shy and wary. It tends to be a
nocturnal creature and generally only leaves its burrow
in the early morning and evening.
The platypus sleeps in a burrow for up to 17 hours a day. The average camping burrow is 1 - 3 meters longs with the entrance hidden underwater or just above the water level. An adult platypus uses its long claws to dig through the soft river banks. It is calculated that a platypus can dig one meter of tunnel in two hours. Grooming of the fur is very important and is done in the water as well as on the land.
The
male
and
the
female
platypus
reach
sexual
maturity
at
two
years
of
age.
The
male
is
unable
to
produce
sperm and the female is unable to produce eggs until
that time. The breeding season is between August and
October. During the breeding season the timid male
platypus becomes aggressive toward other male
platypuses. It is at this time that the spurs on the
hind legs become venomous and are used to fight for
territory and females. This venom is not fatal to man
but does cause intense pain. Mating is thought to
happen in the water. It is also suspected that
the spurs on the hind legs of the male may be used to
hold the female. Part of the courtship involves
various swimming movements including the female
swimming in a tight circle as the male follows her and
hangs onto her tail with his jaws.
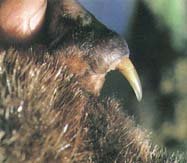 The platypus uses its electro-sensitive bill to locate its food in the water. Once it has food in its bill, it moves the food to its cheek pouches located behind the bill. When the platypus returns to the surface, it moves the pouch contents back to its bill. Then the platypus grinds the food using its grinding pads on the upper and lower jaws. Unwanted parts of food, such as shells, mud, etc are expelled through the horny serrations located on the sides of the lower jaw.
The platypus is capable of making noises. These noises have been compared to a a growling puppy to an angry hen. The young platypuses use these noises to call playmates and the adults use them to contact neighbors. These calls are made with a larynx typical of a mammalian laryngeal skeleton. |

|
|
|
ATTRIBUTES |
|
|
|